應用功能 & 儀器規格
應用功能:
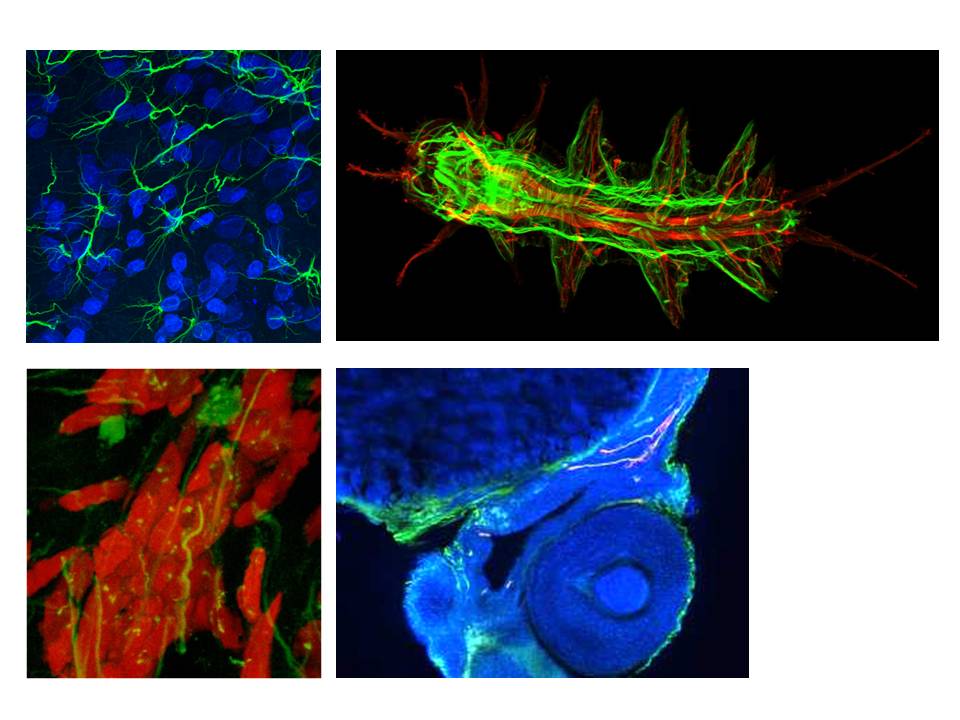
1. 一般螢光樣品與活細胞培養皿影像拍攝。
2. 多點位置記憶掃圖。
3. 大面積影像掃描。
4. Photobleaching,Photoconversion 等操作實驗。
5. 定性、定量分析處理
儀器規格:
1. 顯微鏡系統:Axio Observer Z1倒立式顯微鏡。
2. 雷射波長:405nm、488nm、555nm、639nm。
3. 物鏡倍率:5X、10X、20X、40X(油鏡)、63X(油鏡)
4. 配有 DIC 影像
5. 具電動載物台,可多點位置記憶掃圖與大面積影像掃描。
Introduction:
The focal point of the objective lens in a microscope is reformed into a “conjugate” focal plane close to the detection system. By inserting an aperture diaphragm (Pinhole) in this conjugate focal plane, we can obstruct fluorescence emission from planes OUTSIDE of the primary focus point.
• Point source laser is scanned in raster pattern over sample using Galvanometric mirrors
• Galvo Mirrors move beam in X and Y dimensions for EVERY pixel in the digital image
• Intensity values (within a 12 bit dynamic range) are recorded by PMT for every pixel
Function(application):
•Diode laser 405nm; 488nm; 555nm ;639nm
•Plan-Apochromat 5x,NA0.16;Plan-Apochromat 10x,NA0.45;Plan-Apochromat 20x,NA0.8;Plan-Apochromat 40x,NA0.95;Plan-Apochromat 63x,NA1.4
Experimental Items:
• Multi-fluorescent specimens with distinguishable three dimensionality
• Samples that require localized exposure
• Photobleaching Experiments (FRAP)
• Time series Experiments
• Samples with overlapping probes (META)
儀器放置位置
國際學術研究大樓 八樓 IR808室 - 生物醫學影像核心研究室
生物醫學影像核心研究室 全景圖
申請流程 & 教育認證
申請流程:
自行上機:
1. 須通過本中心辦理之兩階段認證考試合格後,使用者方可預約時段自行操作,並負責儀器安全。
2. 欲操作之使用者,請先與本中心操作管理人員預約時段。
3. 下載申請表單及填妥,並詳閱儀器使用規則。
4. 使用完畢後,操作管理人員會依照使用時數開立繳費單,請使用者持繳費單至本校出納組繳費後,將繳費單繳回操作管理人員。
開放時段:
每日分為:08:00 ~ 11:00、11:00 ~ 14:00、14:00 ~ 17:00 三個時段 (3小時為一個時段)。
教育認證:(113.11.06_第二次中心會議通過)
一、常規認證(兩台共軛焦顯微鏡交錯辦理,約3個月舉辦一次)
1.條件:需自行操作儀器者
2.收費:免費
3.認證流程:
a.參與中心舉辦之教育訓練課程,並登記通過筆試測驗。
b.課程包含實機操作之講解,後續通過實機操作考試。
c.通過後,半年內使用者須進行第一次預約上機,向認證之種籽師資安排時間,並委請陪同上機,俟種籽師資確認操作無誤、通過考核後,即可自行預約操作上機。
二、急件認證
1. 條件:急需自行操作儀器者,可委託技術人員單獨額外教學。
2. 收費:教學認證時段(3小時)及第一次陪同上機時段(3小時),將依委託上機費用(2500元/3小時)進行收費。
3. 認證流程:
a.先行線上觀看課程影檔,並預約現場筆試測驗。
b.通過後,與技術人員預約教學認證時間(課程包含實機操作教學,實機操作練習及考試。)
c.一個月內使用者須進行第一次預約上機,向技術人員預約陪同上機時段,俟其確認操作無誤、通過考核後,即可自行預約操作上機。
附註:若需再增加陪同上機教學時數,另收費1000元/小時
使用規則 & 收費標準
校內使用者:
1. 自行上機:1,200元/3hr。
2. 委託上機:不開放委託上機。
3.當日連續使用2或3時段,收費總價打八折。若使用超過3時段,則當日最高收費以3時段計,隔日第一時段開始則繼續累進計費。
育成中心進駐企業:
1. 自行上機:4,800元/3hr。
2 .委託上機:不開放委託上機。
校外使用者:
1. 自行上機:6,000元/3hr。
2. 委託上機:不開放委託上機。